1.1 General
This test is applicable to enamelled round wire.
Resistance to refrigerant is expressed by the quantity of matter extracted from the coating of
the wire and by the breakdown voltage after exposure to a refrigerant.
NOTE 1 The data in this test method apply to monochlorodifluoromethane (refrigerant R 22). Other refrigerants
that have been determined by investigation to be appropriate for this test are provided in Annex A. When these
other refrigerants are used, it is important for safety reasons to observe the critical data for these refrigerants and
to comply with the revised test conditions during operation of the pressure vessel.
NOTE 2 Refrigerants like monochlorodifluoromethane and rinsing fluids like trichlorotrifluorethane (refrigerant
R 1 1 3) are ozone depleting chemicals (ODC). Refrigerant and rinsing fluid are agreed upon between customer and
supplier.
1.2 Extraction
1.2.1 Principle
A siphon cup containing the wire sample is placed in the pressure vessel. The extractable
matter is determined after exposure of the wire sample to the refrigerant under pressure and
at elevated temperature.
1.2.2 Equipment
The following equipment shall be used:
- siphon cup according to Figure 2, of 450 ml volume up to the siphoning level;
- pressure vessel of 2 000 ml volume with an internal diameter of approximately 1 00 mm
and a pressure capacity of 200 bar (20 MPa), preferably of unwelded construction and
provided with a controlled heating system;
- top closure of the vessel containing a condenser coil according to Figure 3;
- oven with forced air circulation.
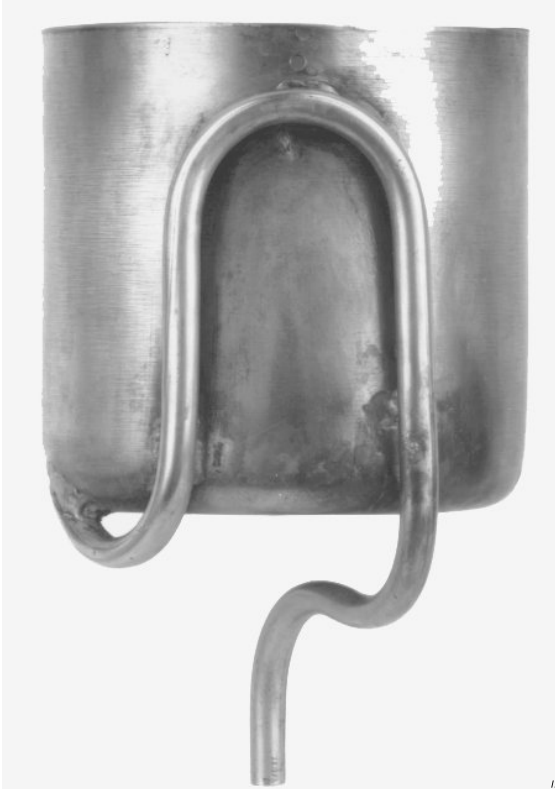

Key
Height of cup: (82 ± 5) mm
Diameter of cup: (84 ± 5) mm
Diameter of tubing: (5 ± 1 ) mm
Figure 2 – Refrigerant extractable test siphon cup
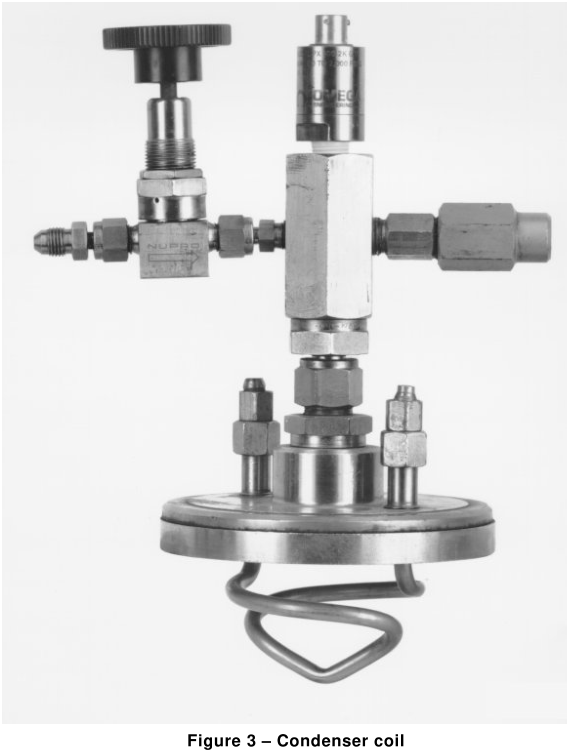

1.2.3 Specimen
Eight wire samples each containing (0,6 ± 0,1 ) g of insulation shall be wound into coils of
70 turns. The specimens shall be degreased and conditioned in an oven with forced air
circulation at (1 50 ± 3) °C for 1 5 min. After 30 min cooling, the eight specimens shall be
weighed together to the nearest 0,000 1 g, resulting in the total initial mass M1 .
1.2.4 Procedure
The eight specimens shall be placed in the siphon cup, which is suspended (25 ± 5) mm
below the condenser coil on the pressure vessel cover. The pressure vessel shall be
assembled and charged with (700 ± 25) g of distilled refrigerant free from lubricant. The
condenser water supply and drain line shall be connected and the pressure vessel shall be
heated by means of a controlled heating system with the temperature set to (75 ± 5) °C or a
lower temperature if required to comply with the conditions of the following paragraph relating
to critical pressure. The water flowing through the condenser shall be adjusted to maintain a
reflux rate of 20 to 25 discharges per hour from the siphon cup. The extraction period shall be
6 h
The pressure in the vessel shall not exceed 75 % of the critical pressure of the refrigerant
chosen. Therefore, prior to use, the over-pressure control valve shall be checked to ensure its
proper functioning. The heating system should be automatically deactivated if the pressure
exceeds 75 % of the critical pressure of the refrigerant chosen or if the water flow through the
condenser coil is interrupted.
At the end of the extraction period the pressure vessel shall be cooled. The refrigerant shall
be removed from the pressure vessel and recovered using suitable means such as a
refrigerant compressor and recovery system. The pressure shall be released and the pressure
vessel opened.
For the following operations, the rinsing fluid shall be distilled before use.
The specimens and siphon cup shall be rinsed with the agreed rinsing fluid, the rinse poured
into the pressure vessel and the walls of the pressure vessel washed with two successive
rinses each of 1 00 ml of rinsing fluid. The fluid shall then be evaporated to (5 ± 1 ) mm from
the bottom of the pressure vessel and recovered in a safe manner.
The liquid sample shall be transferred to a pre-dried tared aluminium weighing dish and the
pressure vessel rinsed with 1 5 ml of rinsing fluid, which is transferred to the dish and then
evaporated to dryness at (1 50 ± 3) °C for (60 to 65) min. The weighing dish shall then be
cooled to room temperature in a desiccator. The dish with the residue shall be weighed to the
nearest 0,000 1 g and the original tared mass of the same dish subtracted. The difference is
the total residue mass M 2 of the matter extracted from the eight specimens.
The insulation on the coils shall be removed by suitable chemical means not affecting the
conductor and the bare conductors shall be dried at (1 50 ± 3) °C for (1 5 ± 1 ) min and cooled
to room temperature in a desiccator. They shall be weighed to the nearest 0,000 1 g and the
mass of the eight conductors together is the total conductor mass M 3 .
1.2.5 Result
The extractable matter shall be determined according to the following equation :
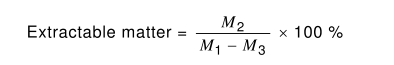
One test shall be made. The masses M 1 , M 2 , M 3 , the refrigerant, rinsing fluid, temperature,
pressure of the pressure vessel and the percentage extractable matter shall be reported.
1.3 Breakdown voltage
1.3.1 Principle
A specimen prepared according to 4.4.1 of IEC 60851 -5:2008 is placed in a pressure vessel according to 4.3.2. The breakdown voltage is determined after exposure of the specimen to the refrigerant under pressure and at elevated temperature.
1.3.2 Procedure
The specimen shall be conditioned in the oven (1 50 ± 3) °C for 4 h and then placed in the pressure vessel, which shall be assembled and charged with (1 400 ± 50) g of refrigerant. The pressure vessel shall be heated according to 4.2.4 but for a period of (72 ± 1 ) h.
At the end of the exposure period, the pressure vessel shall be cooled and discharged as described under 4.2.4. When the pressure inside the tube is less than 2 bar (0,2 MPa) absolute, the pressure vessel shall be opened and the specimen, within a period of 25 s to 30 s, transferred to the oven at a temperature of (1 50 ± 3) °C. The specimen shall remain in the oven for (1 0 ± 1 ) min. After the specimen is removed from the oven and allowed to cool to room temperature, the breakdown voltage shall be determined according to 4.4.1 of IEC 60851 -5:2008.
1.3.3 Result
Five specimens shall be tested. The five individual values shall be reported.
