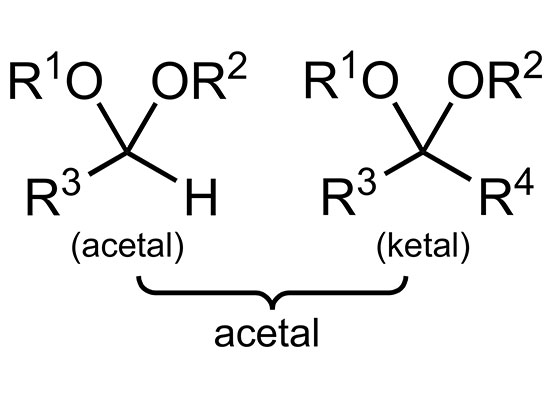
Acetal, a general term for a class of organic compounds, is the product of the condensation of one molecule of aldehyde and two molecules of alcohol, such as acetaldehyde diethyl acetal, with a boiling point of 104 °C; benzaldehyde dimethyl acetal has a boiling point of 207 °C. Acetals generally have a pleasant fragrance. The acetal is easily hydrolyzed into the original aldehyde and alcohol under the catalysis of acid.
Physical properties
1. Properties: Colorless and volatile liquid with aromatic odor.
2. Melting point (℃): -100
3. Boiling point (℃): 102.7
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.83
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 4.1
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 2.7 (20℃)
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -459.4
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 2.98
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.84
10. Flash point (℃): -21 (CC)
11. Ignition temperature (℃): 230
12. Upper limit of explosion (%): 10.4
13. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.6
14. Solubility: soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether, acetone and chloroform.
15. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.3811
16. Flash point (ºC): 230
17. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, 102.9ºC): 32.75
18. Heat of combustion (KJ/kg): 3890
19. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 9~99ºC, constant pressure): 2.18
20. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 0.824241.6
21. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.22
22. Eccentricity factor: 0.432
23. Solubility parameter (J cm-3) 0.5: 16.506
24. Van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 1.083×1010
25. van der Waals volume (cm3 mol-1): 75.650
26. Standard combustion heat of gas phase (enthalpy) (kJ mol-1): -3908.3
27. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ mol-1): -453.5
28. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ mol-1): -3870.49
29. Liquid phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ mol-1): -491.4
Chemical Properties – Stability
1. Chemical properties: The stability is smaller than other ethers, and there is a tendency to polymerize when placed. It is stable to alkali, but can also be hydrolyzed into acetaldehyde and ethanol with weak acid at low temperature; react with hydrogen iodide gas to generate iodoethane and acetaldehyde; generate acetic acid when oxidized. Stable in alkaline. When on fire, use carbon dioxide, carbon tetrachloride or dry chemical fire extinguishing agent to put out the fire, water is ineffective.
2. Stability: Stable.
3. Incompatible substances: strong oxidants, acids.
4. Conditions to avoid: air, light.
5. Polymerization Hazard: Do not polymerize.
Acetal enameled wire
Acetal enameled wire is one of the earliest developed varieties in the world. It has been put on the market by Germany and the United States in 1930. The Soviet Union is also developing rapidly. There are two kinds of polyvinyl formal and polyvinyl acetal. my country is also in 60 The age study was successful. Although the enameled wire has a low temperature resistance level (105°C, 120°C), it is widely used in oil-immersed transformers due to its excellent high temperature hydrolysis resistance. This characteristic has been notarized by countries all over the world. There is a small amount of production, especially the acetal enameled flat wire is used to make transposed conductors, which are used in large transformers
